
The internet has grown with other information technologies; arguably the most popular technology. With an infinite connection of people from different locations and backgrounds surfing the internet every day via the web, the internet presents a platform for information dissemination at a flash speed, relative to pre-existing means. Together with these pre-existing and emerging information technologies, the internet has made information spread at amazing speed.
Functioning as an application layer protocol running on the internet, the web is home to many ideas and many innovations, it has formed a huge part of the internet age. To many; the internet age is championed by the web. This is not far from the fact anyways.
Computer programming languages have enabled the creation of utilities on the web. It is hence not only a protocol on the internet, it has become quite home to everyone who has access to the internet, well-crafted gadgets have also been developed to enable more enhanced and efficient web functionalities.
‘The World Wide Web’ takes you to a world of infinite possibilities and opportunities.
During its first generation, the web was mainly a hub of information and ‘documents’. Simply, a platform hosting information written in the hypertext markup language (HTML), with little or no user interaction with the website.
The emergence of more advanced programming languages including HTML and also the evolution of the computer and the internet enabled the creation of web platforms with more user interactivity. A web platform where users can interact with the website to a very large and also with other users visiting the website, thus the birth of Web 2.0
Coined by Darcy Dinucci in 1991 to imply a second generation of the web evolution; the term ‘web 2.0’ is a collaborative and participative web platform that allows its users to perform social activities on the web such as generating their own content and interacting with content generated by other users of the platform and also with the users who generated this content.
Several web 2.0 applications have had a major influence on our everyday life. From blogging platforms to video hosting and sharing platforms where users can interact with content, generate and share their own content. With the web 2.0 resources, commercial applications have been built on the Web, and information from a web 2.0 platform can be distributed to and used by other platforms via information distribution algorithms such as web APIs and RSS (RDF Site Summary)
Web 2.0 platforms are hosted on a server with one entity controlling activities on the platform. This control is unlimited and spans almost every aspect of the platform including content generation and information distribution on the platform, personal profile creation, and personal profile details.
Owners of these platforms hence possess total control of the platform. This serves some positive purposes as owners of the platform can easily control activities on the platform to ensure that it complies with the terms and conditions specifications. This ability to censor content generated on web 2.0 platforms leaves users with the role of ‘mere participants’ who hold almost zero control over how they are treated on the platform.
On the dark side, owners of web 2.0 have in many instances misused their access to every activity on their platforms including confidential information about the users of the platform. Information about topics of interest has also been censored or put down by the controllers of these platforms in cases where such information is against their interests or gives put vital information on some issues which expose certain parties related to the platform.
Having known the enormous influence information has on the audience, parties directly concerned with a subject and other interested parties tend to modify information reaching out to the audience as regards the subject. Putting away some aspects of the information going out, modifying it to suit their interests; and in most cases Suppressing others who have access to more knowledge about the subject from sharing this information. If there’s any specie in the information age that has been endangered by web 2.0, it is the freedom of speech.
While the centralized internet has arguably created a healthy internet, its dark side is big enough to override these imagined regulations. Cryptocurrency speakers and enthusiasts are currently having a rough time with video hosting platforms as well as blogging platforms. Articles and videos related to cryptocurrency are being censored and put down and in some cases, their profiles on these platforms are banned or restricted as the case may be.
This simply attacks a topic of interest that people needs to have the right information about, while topics like this do not pose any threat to human life or negatively disrupt existing information, many harmful activities and contents are left to float on these platforms.
Failure of web 2.0 in these aspects has once again left internet users scrambling for a healthier environment where they hold some or at least, total authority over how their generated contents and personal information are handled by the administrators of the platform — a decentralized platform where users are in charge of themselves and others have almost no direct control over their activities.
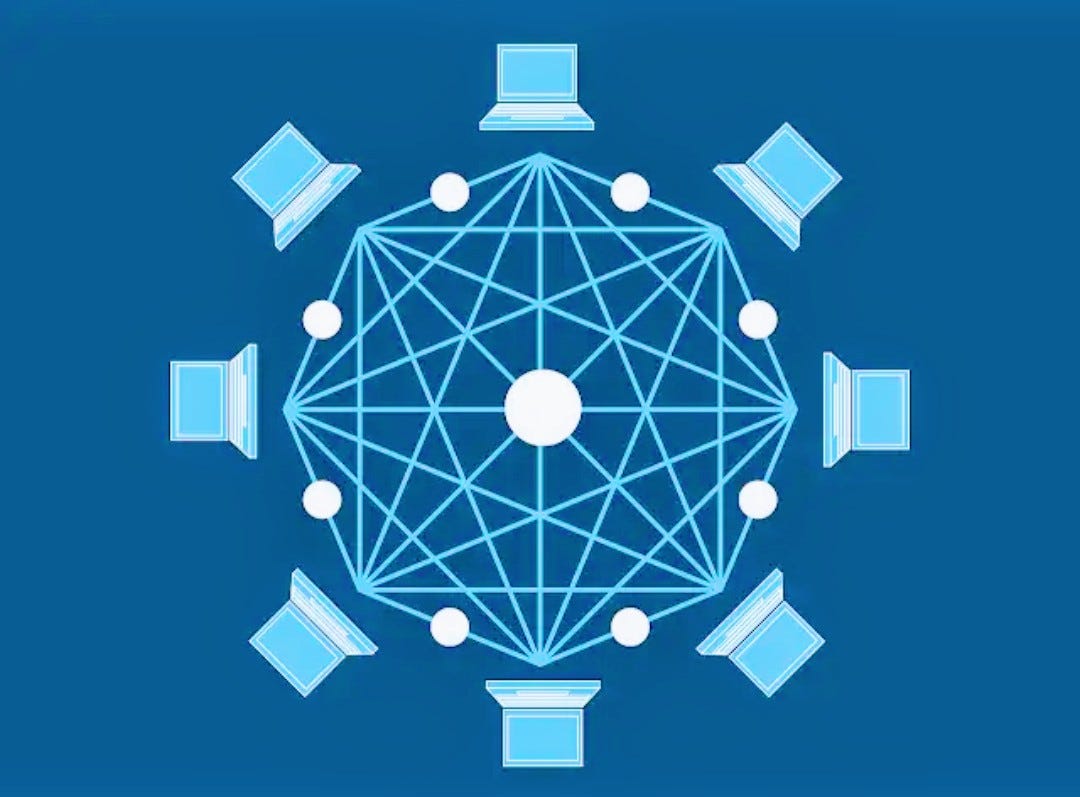
In a decentralized internet; each user is like a well-fenced building in an estate and each building is fenced individually with another common fence protecting the whole estate. This depicts an independent platform where the users are independent of the administrators and other users as each profile is hosted differently on the platform.
In contrast to centralized platforms, decentralized web platforms present a disseminated governance system where each member has tangible control of their activities. Decentralized web platforms are also known as WEB 3.0 platforms.
Web 3.0 technologies redefine the back end of the web. They distribute equal rights to each user while the web front end remains relatively the same and the front end works as usual. The back end of the internet is structured to serve equal rights to users.
The web 3.0 revolution is led/enabled by blockchain technology. The blockchain is a ‘chain of blocks’, Blocks are permanent stores of immutable data/information. These include information such as agreements between the parties in the transactions; the name of the sender, name of the recipient, and the amount transacted.
A block could store just any information, in cryptocurrency transactions which is the most popular context of blockchain applications, a block holds records of all recent transactions.
For new information to be stored, a new block must be created. The new block is referenced to the previous block, information cannot be added to the previous blocks and its information cannot be edited.
Each block contains a record of data and an identical hash (a cryptographic code) that identifies the block. To ensure more security and stability of the blockchain, the blockchain servers (node) are run by each user of the blockchain, every user running a node verifies each block before it is created.
Web platforms built on the blockchain copy this concept too. Each user who creates an account on the platform owns an account that runs on the blockchain. Activities by each user are verified by other users and are stored on the block. The block is immutable, hence these activities including contents generated by the user and the user profiles are stored permanently on the blockchain and cannot be censored or removed completely from the blockchain. This solves the problem created by the centralization of the web in web 2.0.
Web 2.0 platforms continue to wallow in centralization and censorship by administrators of these platforms as complaints from content creators on these platforms continue to rise. Emerging web3 platforms on the other hand have delighted their users with their immutability and decentralization. Content creators on these platforms are rest assured of the safety of the content they generate as well as the safety of their platforms which they have worked so hard to build.

Web3 platforms offer immutability and censorship resistance, one would wonder how it regulates unhealthy activities on the platform…
Web 3.0 technologies create multiple points of entry to platforms and as well, multiple control units. These units are in fact controlled by the whole users on the network. It employs specialized algorithms and technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) protocols to ensure that the system works for the users just the way they (individually) want it.
Like a ‘plug and play’ system, connecting your wallet to a platform is all you need to experience a world of possibilities. Web3 platforms preserve user identity and data.

That being said, most web 3 platforms also offer a flexible means of remuneration — Cryptocurrency. Depending on the blockchain platform where a Web3 platform is hosted, participants in the network can be rewarded using native cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrencies are cryptographic tokens that run on a blockchain. They are flexible stores of value. Most blockchains, enable users to access certain features of the blockchain. These tokens can be easily transferred from one user to another. In contrast to certain web 2.0 platforms, this flexible means of remuneration relieves the users of the huge stress they go through to monetize the contents they create on web 3.0 platforms. Given the ability to monetize (most forms of) participation on web3 platforms, interactivity on the web is enhanced as every user is incentivized to participate in form of creating content or interacting with the platform itself.
The future is ‘decentralized’. Some Web 3.0 projects are developing decentralized versions of existing internet facilities including VPNs, SDKs, and Routers. This extra equipment in synergy with websites built on distributed networks will power the next generation of the web and internet.
A major barrier to web 3.0 adoption is the complexity of these platforms and the fact that most blockchains currently do not (or poorly) scale. The pronounced complexity makes it hard for average tech enthusiasts to use these platforms. Blockchain as a concept is still emerging and a majority are yet to grasp how it actually works.
Unable to scale, most blockchains are ‘heavy’ and get even heavier as more users adopt their technology. This decreases efficiency…a major turn-off. Nevertheless, there’s still a long way to go for a concept as young as Web 3.0
Leave a Reply